Designing an efficient warehouse layout is crucial for wholesalers aiming to optimize their operations. The warehouse’s layout can have a big impact on how items are handled. It can affect the receiving, storing, picking, and shipping processes. This, in turn, can affect productivity, safety, and the ability to expand.
A good warehouse layout design ensures smooth workflow, minimizes costs, and supports future growth. This guide provides comprehensive insights into designing a warehouse that is not only efficient, but also safe and scalable.
This article will discuss different warehouse layouts, important factors to consider when choosing a layout, the advantages and disadvantages of each layout, and tips for designing a warehouse that meets your needs.

Areas in a Warehouse Layout Design
A well-organized warehouse typically includes several distinct areas, each serving a specific function to ensure efficient operations. Here are the different areas commonly found in a warehouse:
1. Receiving Area
- Purpose: Where goods are initially received from suppliers.
- Features: Unloading docks, inspection stations, and space for initial sorting.
- Considerations: Sufficient truck space, efficient unloading processes, and accurate documentation.
2. Storage Area
- Purpose: Where goods are stored until needed.
- Features: Shelving, pallet racks, bulk storage, and specialized storage (e.g., temperature-controlled areas).
- Considerations: Maximize space utilization, easy access, and organization for different types of inventory.
3. Picking Area
- Purpose: Where items are picked for order fulfillment.
- Features: Shelves or bins for small items, pallet racks for larger items, picking carts, and order lists.
- Considerations: Optimize for efficient picking routes, minimize travel time, and ensure accuracy.
4. Packing Area
- Purpose: Where picked items are packed for shipping.
- Features: Packing tables, materials (boxes, tape, packing peanuts), labeling machines.
- Considerations: Sufficient space for multiple packers, organized packing materials, and quality control checks.
5. Shipping Area
- Purpose: Where packed orders are prepared for dispatch to customers.
- Features: Loading docks, staging areas for outgoing shipments, and shipping documentation.
- Considerations: Efficient flow from packing to loading, access to various shipping carriers, and accurate shipping labels.
6. Staging Area
- Purpose: Temporary holding area for goods that are being processed, picked, or shipped.
- Features: Open space with easy access to other areas.
- Considerations: Flexibility to handle varying volumes and quick turnover.
7. Returns Area
- Purpose: Where returned goods are processed.
- Features: Inspection stations, designated storage for returns, and areas for repackaging or refurbishing.
- Considerations: Efficient handling of returns to minimize delays and accurate record-keeping.
8. Quality Control Area
- Purpose: Where goods are checked for quality and accuracy.
- Features: Inspection tables, testing equipment, and documentation stations.
- Considerations: Ensure thorough inspections and maintain high-quality standards.
9. Office Area
- Purpose: Administrative functions related to warehouse operations.
- Features: Offices for managers and administrative staff, meeting rooms, break areas.
- Considerations: Proximity to operational areas for easy coordination and communication.
10. Maintenance Area
- Purpose: Where equipment and machinery are maintained and repaired.
- Features: Tool storage, workbenches, and spare parts inventory.
- Considerations: Ensure quick access to tools and parts to minimize downtime.
11. Cold Storage Area
- Purpose: For storing temperature-sensitive goods.
- Features: Refrigeration units, temperature monitoring systems, and insulated doors.
- Considerations: Maintain consistent temperatures and monitor compliance with health and safety standards.
12. Safety and Compliance Area
- Purpose: Ensure safety protocols and compliance with regulations.
- Features: First aid stations, safety equipment storage, and emergency exits.
- Considerations: Clearly marked and easily accessible, as well as regular safety drills and equipment checks.
13. Value-Added Service Area
- Purpose: For additional services like kitting, labeling, or assembly.
- Features: Workstations, labeling machines, and packaging materials.
- Considerations: Efficient workflows and clear separation from main storage and picking areas to avoid disruptions.
14. Employee Break Area
- Purpose: A dedicated space for employees to rest and take breaks.
- Features: Tables, chairs, vending machines, kitchen facilities.
- Considerations: Comfortable and clean environment, located away from operational areas to ensure relaxation.
Each area plays a crucial role in warehouse operations’ overall efficiency and effectiveness. Properly designing and organizing these areas can significantly enhance workflow, reduce errors, and improve productivity.

Types of Warehouse Layout Design
Warehouse layouts are crucial for organizing space, improving efficiency, and ensuring safety. The right design can significantly impact how goods flow through the warehouse, from receiving to shipping. With this, there are three typical warehouse blueprints:
- Straight-Line Layout
- U-Shaped Layout
- L-Shaped Layout
Straight-Line Warehouse Layout Design
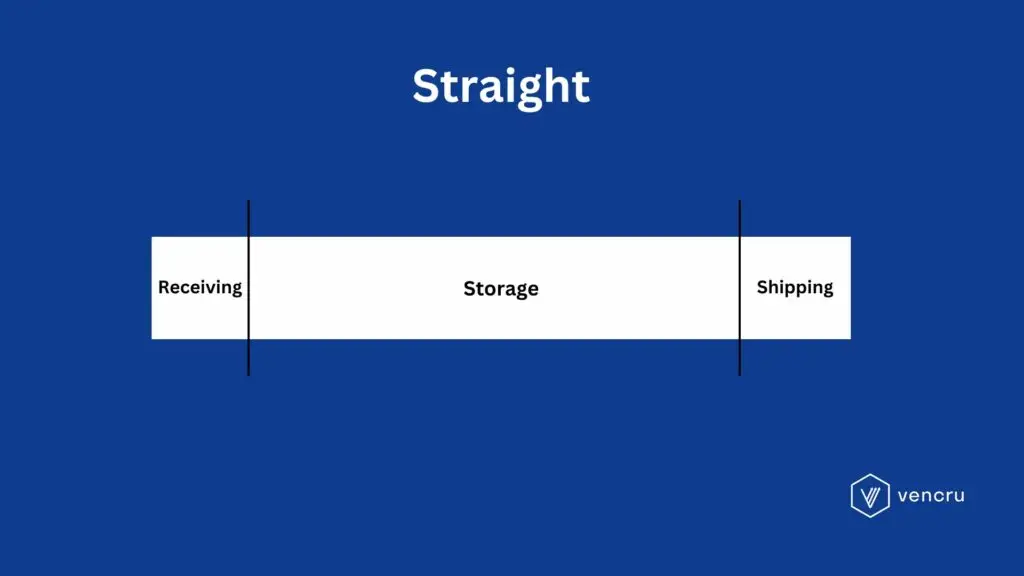
This layout works best for simple, straight processes, like small warehouses. It’s good when the workflow is easy and doesn’t need a lot of sorting, staging, or complex handling.
When to Consider Straight-Line Warehouse Layout Design
- Consistent Workflow: If your warehouse operations involve a straightforward, linear process from receiving to shipping, a straight-line layout can optimize this flow. For Example, In a bakery distribution center where ingredients are received, products are baked, packaged, and shipped out continuously.
- Small Spaces: In smaller warehouses where space is limited, a straight-line layout can maximize the efficient use of available space.
- High Turnover of Similar Products: A straight-line warehouse layout program benefits warehouses with a high turnover of similar or standardized products.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Straight-Line Warehouse Layout Design:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Clear Workflow: Easy to understand and manage. | Limited Flexibility: Not ideal for complex operations requiring multiple stages of handling or processing. |
| Reduced Handling: Minimizes the need to move goods back and forth. | Scalability: This can become inefficient if the volume of goods or complexity of operations increases. |
| Efficiency: A straightforward path reduces the time goods spend in the warehouse. |
U-Shaped Warehouse Layout Design
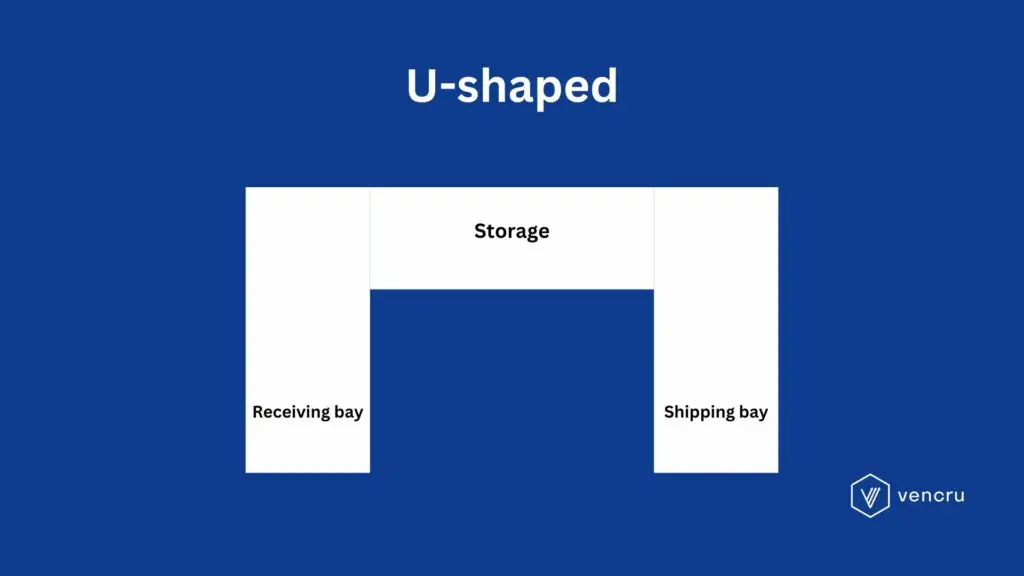
A U-shaped layout is the way to go if you need efficient warehouse space, centralized warehouse management, and quick transitions between receiving and shipping areas. The U-shape design can optimize available space and reduce unnecessary movement of goods. Plus, it allows for a centralized location of the operational area, improving coordination and control.
When to Consider U-Shaped Warehouse Floor Plan
- Maximized Space: The U-shaped layout is ideal for optimizing the use of available space, as it allows for efficient placement of storage and operational areas.
- Smooth Flow of Goods: This layout supports a seamless flow from receiving to storage, picking and packing, and shipping, reducing unnecessary movement.
- Centralized Supervision: The central location of the operational area in a U-shaped layout allows managers to oversee all activities, improving coordination and control easily.
- Efficient Receiving and Shipping Areas: In a U-shaped layout, receiving and shipping areas are located near each other, facilitating quick transitions and reducing transportation times within the warehouse.
- Handling Various Product Types: This layout is adaptable to warehouses that handle a diverse range of products. This allows for dedicated zones for different categories.
Advantages and Disadvantages of U-Shaped Warehouse :
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Efficient Use of Space: Optimizes the use of available space, making it suitable for warehouses with limited square footage. | Potential Congestion: High-traffic areas near the receiving and shipping zones can become congested. |
| Improved Supervision: Centralizes activities for easier oversight and management. | Complexity in Design: Requires careful planning to ensure smooth workflow and avoid bottlenecks. |
| Efficient Use of Space: Optimizes available space, making it suitable for warehouses with limited square footage. |
L-Shaped Layout Warehouse Layout Design
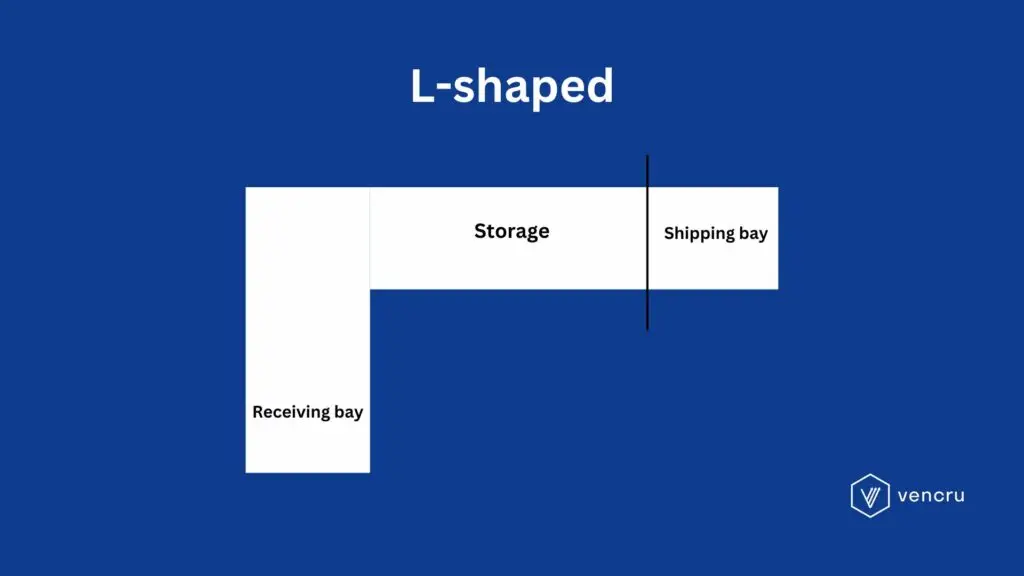
The L-shaped layout stands out because it can accommodate a wide range of needs and adapt to irregular spaces. This layout shines when it comes to streamlining operations, enhancing inventory management, and effectively handling diverse product lines. Additionally, it excels at maintaining a clear separation between the receiving and shipping areas, making it an ideal choice for warehouses seeking such a feature.
When to Consider L-Shaped Warehouse Layout
- Separation of Functions: The L-shaped layout separates the receiving and shipping areas, which can reduce congestion and streamline processes.
- Adapting to Space Constraints: This layout is ideal for warehouses located in buildings with irregular shapes or when using an oddly shaped property best.
- Zoning for Product Types: Allows the creation of distinct zones for different product lines, facilitating better organization and management.
- Streamlined Operations: The L-shaped layout can streamline operations by reducing the travel distance between key functional areas while keeping operations organized.
- Better Inventory Segmentation: Facilitates better segmentation and management of inventory, especially useful for warehouses with varied stock-keeping units (SKUs).
Advantages and Disadvantages of L-Shaped Warehouse Layout Design:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Reduced Congestion: Separates receiving and shipping areas to minimize traffic congestion. | Complex Navigation: This can be more complicated than straightforward layouts. |
| Efficient Space Utilization: Makes the best use of irregular or non-standard spaces. | Potential for Inefficiency: The layout can lead to inefficient movement between zones if not well-planned. |
| Organized Workflow: Enhances workflow efficiency by logically separating different operational areas. |
Conclusion
Designing an efficient warehouse layout is crucial for optimizing operations, ensuring safety, and supporting future growth. By understanding the different types of layouts, considering key factors, and following best practices, wholesalers can create a warehouse that meets their needs both now and in the future.
Investing in a warehouse layout design is a strategic decision that lays the foundation for long-term success in the competitive world of wholesale distribution. Continuously improving and adapting your warehouse design will ensure it remains effective as your business evolves.






