If you’ve ever lost a sale because you ran out of stock, spent hours chasing down payments, or found yourself buried in spreadsheets just trying to figure out which orders were shipped or paid for, you’re not alone. A poor order management process is often the hidden culprit behind cash flow issues, missed growth opportunities, and day-to-day stress.
Order management isn’t just about fulfilling a sale. It’s about controlling your business’s entire flow of money and inventory, from when an order is placed to when payment hits your account. A sloppy order process leads to late shipments, lost revenue, overstocked shelves, and unpaid invoices.
In this guide, “Order Management 101, we’ll walk you through the essentials, step by step. The goal is to help you build an efficient system that boosts your cash flow and sets your business up for scalable growth.
What is Order Management and Why Does It Matter?
The order management process encompasses an order’s complete journey, from the moment a customer decides to buy (or you decide to buy from a supplier) until the final payment is settled. Think of it as the backbone of your sales and inventory operations.
The Typical Order Lifecycle & Consequences of Poor Order Management
Understanding the typical lifecycle of an order highlights the critical points where efficiency can be gained or lost:
- Purchase Order (PO): You create a PO to buy goods from your suppliers.
- Goods Receiving: The items arrive, and you log them into your inventory.
- Sales Order (SO) / Quote: A customer places an order, or you send them a quote, which they accept.
- Order Fulfillment: You pick, pack, and ship the items to your customer.
- Invoicing: You send an invoice to the customer for their order.
- Payment Collection: The customer pays, and you record the payment.
When done right, order management becomes the engine of your operations, keeping your shelves stocked, customers happy, and cash flowing. However, when handled manually—across notebooks, spreadsheets, or scattered apps—it can seriously hurt your business, leading to:
- Tied-Up Cash: Excess stock sits on your shelves, locking up money you could use elsewhere.
- Late Shipments: Disorganized processes lead to delays, frustrating customers.
- Delayed Payments or Uncollected Invoices: If you don’t invoice promptly or track payments, your cash flow suffers.
- Customer Churn: Poor experiences (late orders, wrong items) drive customers away.
- Wasted Time & Resources: Manual tracking and fixing mistakes eat up valuable time.
Getting order management right means smoother operations, happier customers, and a healthier bottom line.
The Core Components of an Efficient Order Management Process
To grow sustainably, you need a simple, repeatable order process that works whether you’re fulfilling 10 or 1,000 orders a month. Understanding each stage helps identify areas where improvements can significantly impact your cash flow. Let’s break it down into six essential stages every business should master:
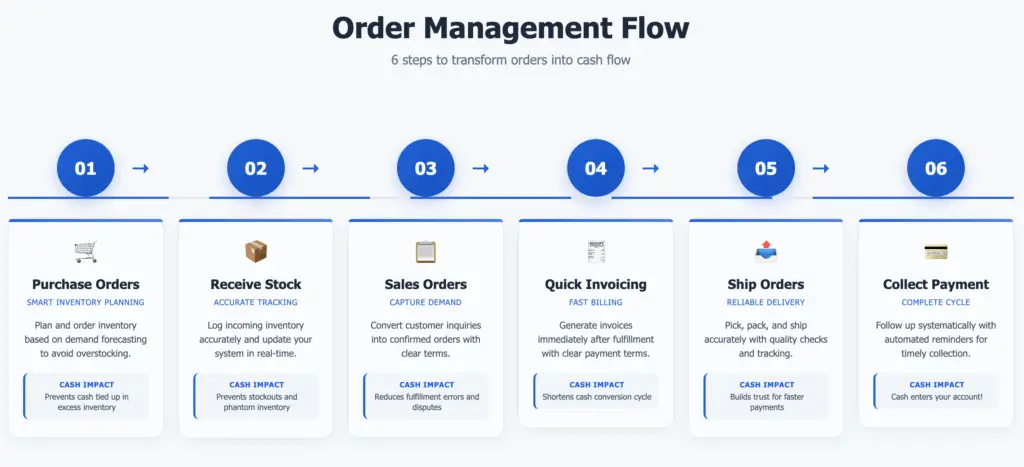
| Stage | Description | Cash Flow Impact |
| 1. Purchase Orders | Record what you buy from suppliers. | Avoids overbuying and prevents cash from being tied up in unnecessary stock. Helps prevent stockouts for popular items. |
| 2. Receiving Stock | Log inventory into your system when goods arrive. | Keeps inventory levels accurate, preventing overselling and ensuring you know what cash is tied to stock. |
| 3. Sales Orders/Quotes | Confirm orders with customers or have them accept quotes. | Helps track demand early, allowing for better inventory planning and cash flow forecasting. |
| 4. Invoicing | Turn sales orders into invoices quickly. | Shortens the time to payment; the sooner you invoice, the sooner you can get paid. |
| 5. Fulfillment | Pick, pack, and ship efficiently and accurately. | Increases customer satisfaction (leading to repeat business) and reduces costs from errors or returns. |
| 6. Payment Collection | Match payments to invoices and follow up. | Ensures you’re actually getting paid for your goods and services, directly boosting cash inflow. |
Related: What Is a Purchase Order?
Common Mistakes Small Businesses Make (And How to Avoid Them)
Navigating order management can be tricky, and many small businesses encounter similar hurdles. Identifying these common pitfalls is the first step to avoiding them and protecting your bottom line:
| Mistake Title | Description | How to Avoid It |
| Relying on Spreadsheets and Notebooks | While okay for starting, these quickly become unmanageable, error-prone, and don’t offer real-time insights. | Exploring simple, affordable order management tools designed for small businesses. Even basic digital solutions offer significant advantages over manual methods in saving time and reducing errors. |
| Failing to Link Inventory with Sales | This is a classic recipe for stockouts (selling items you don’t have) or overstocking (not knowing what’s selling well). | Implementing a system where inventory automatically syncs with sales. This ensures accurate stock counts, preventing lost sales from stockouts and wasted capital on overstock. |
| Forgetting to Follow Up on Payments | Assuming customers will pay on time without reminders can lead to significant cash flow gaps. | Setting up a consistent follow-up schedule for overdue invoices, perhaps with templated email reminders for different stages (e.g., 3 days past due, 1 week past due). Automation features in many tools can be a huge time-saver here. |
| Not Tracking Supplier Performance | Late deliveries or incorrect orders from suppliers can disrupt your entire workflow and ability to serve customers. | Keeping records of supplier reliability and addressing issues proactively. |
| Mixing Up Backorders, Partial Shipments, and Cancellations | Poor tracking of these exceptions leads to confusion, customer dissatisfaction, and inaccurate inventory. | Establishing clear, written procedures for handling backorders, partial shipments, and cancellations, and using a system that clearly flags and tracks these statuses. This improves internal clarity, maintains transparency with customers, and keeps inventory data reliable. |
The Role of Technology in Streamlining the Order Management Process
Many small business owners hear “software” and think of big, complex, and expensive Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. The good news is you likely don’t need an ERP—just software built for your business’s size and specific needs.
Look for small business-friendly tools with features like:
- Sales and Purchase Order Tracking: Create, manage, and track both SOs and POs in one place.
- Real-Time Inventory Sync: Your inventory levels should update automatically as sales are made and stock is received.
- Quote → Invoice Conversion: Easily turn a sales quote into an invoice with a click, saving time and reducing errors.
- Payment Tracking: See which invoices are paid, unpaid, or overdue at a glance.
- Mobile Access: Manage orders and check inventory from your phone or tablet on the go.
- Integration with Accounting Software: Smoothly sync your sales and payment data with tools like Vencru, QuickBooks, Xero, etc.
These features can dramatically reduce manual work, minimize errors, and give you a clear view of your operations. Many easy-to-use order management tools are designed specifically for small businesses, helping manage orders, inventory, invoicing, and payments seamlessly.
Transforming Orders into Cash Flow: The Benefits of Optimization
This is where the magic happens! Efficient order management directly fuels your cash flow and enables sustainable growth.
How Better Order Management Improves Your Cash Flow:
- Faster Order-to-Cash Cycle: The quicker you can turn an order into a paid invoice, the faster that cash is back in your bank account, ready to be reinvested or cover expenses.
- Better Inventory Control = Less Capital Locked Up: Knowing exactly what stock you have, what’s selling, and what’s not helps you avoid tying up precious cash in slow-moving or obsolete inventory. You buy smarter.
- Automated Reminders = Reduced Late Payments: Systems that send automatic payment reminders mean you spend less time chasing invoices and get paid more consistently.
- Accurate Stock Forecasting = Smarter Purchasing: Understanding sales trends (thanks to good order data) allows you to predict future demand better. This means ordering the right amount of stock at the right time, optimizing your purchasing budget.
Connecting Improvements to Financial Results:
Understanding how order management improvements translate to financial results helps justify the time and resources invested in optimization.
- Faster Processing = Faster Payment: Reducing the time between receiving an order and shipping it allows you to invoice sooner. Invoicing just one day faster across all orders can improve monthly cash flow by thousands of dollars for most small businesses.
- Reduced Errors = Lower Costs: Every order error costs money through return shipping, replacement products, customer service time, and potentially lost customers. Reducing errors from 5% to 1% can save substantial money annually.
- Better Inventory Management = Improved Capital Efficiency: Optimized inventory levels mean less cash tied up in slow-moving stock, fewer missed sales from stockouts, reduced storage costs, and potentially better supplier terms through more predictable ordering.
- Automation = Lower Labor Costs: Automated processes reduce staff time needed for manual data entry, invoice generation, payment follow-up, and routine administrative tasks.
How Smooth Order Management Processes Enable Growth:
- Scalability Without Chaos: Well-designed processes let you handle significantly more order volume without proportionally increasing staff or complexity.
- Improved Customer Experience Drives Loyalty: Customers who receive accurate orders on time with good communication become repeat buyers and refer others.
- Owner Time Freedom: When order management runs smoothly, business owners can focus on strategic growth initiatives instead of constantly fighting operational fires.
- Competitive Advantage: Reliable order fulfillment becomes a competitive differentiator. Customers will pay more and remain loyal to suppliers they can count on.
Key Strategies for Optimizing Your Order Management Process
Your order management process doesn’t have to be perfect overnight, but it does need to be intentional. The following strategies will help you transform chaotic order handling into a systematic approach that drives cash flow and supports growth.
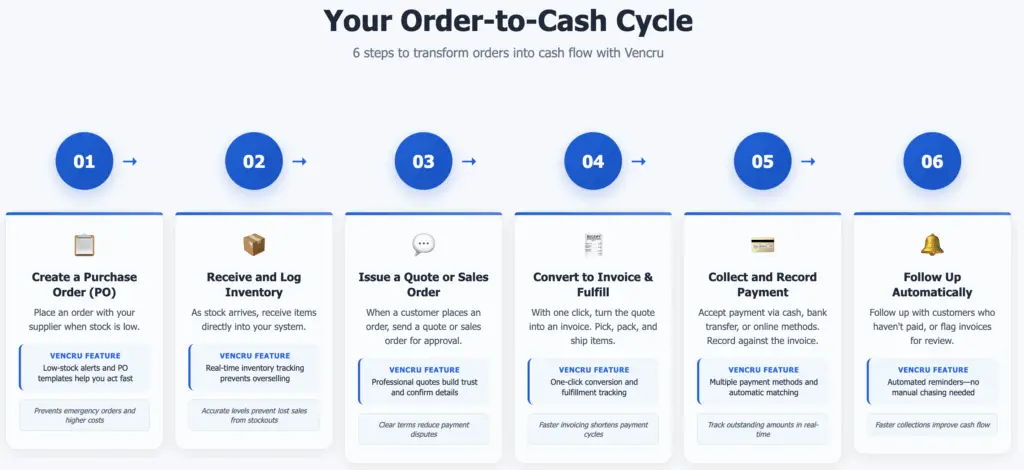
Your Order-to-Cash Cycle – 6 steps to transform orders into cash flow
A. Establish a Simple, Repeatable Order Workflow
If you’re running a small retail or wholesale business, the key to scaling isn’t working harder—it’s creating workflows that run effectively, often without direct daily intervention. A good order management system doesn’t just track what’s coming in and going out; it builds repeatable habits into your business, so every team member knows what to do next.
Here’s how to set up a simple, streamlined workflow from purchase to payment:
🔁 Your Order-to-Cash Cycle in 6 Steps:
- Create a Purchase Order (PO): Place an order with your supplier when stock is low. Vencru’s low-stock alerts and PO generator help you act fast.
- Receive and Log Inventory: As stock arrives, receive items directly into your system. This keeps inventory levels accurate and prevents overselling.
- Issue a Quote or Sales Order: When a customer places an order, send a quote or sales order for approval, building trust and confirming order details.
- Convert to Invoice & Fulfill the Order: With one click, turn the quote into an invoice. Pick, pack, and ship items—then mark as fulfilled in the system.
- Collect and Record Payment: Accept payment via cash, bank transfer, or online methods. Record payment against the invoice to track what’s outstanding.
- Follow Up Automatically: Vencru helps you follow up with customers who haven’t paid, or flag invoices for review—no manual chasing needed.
📌 Pro Tip: Use the same workflow for every order. It minimizes errors, saves time, and ensures nothing falls through the cracks. With Vencru, you don’t need to switch between spreadsheets, apps, and memory. Everything from POs to invoices lives in one place—optimized for small businesses that want to stay lean and grow fast.
Use Checklist-Based SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures):
Create simple checklists for routine tasks. This ensures consistency, no matter who is performing the task.
- Daily Stock Check:
- [ ] Review inventory levels for key items.
- [ ] Identify items nearing reorder points.
- [ ] Check for any discrepancies from recent sales or deliveries.
- Weekly Supplier Order Review:
- [ ] Based on stock checks and sales forecasts, determine what needs ordering.
- [ ] Draft and send Purchase Orders to suppliers.
- [ ] Follow up on any outstanding POs.
- Monthly Order and Invoice Audit:
- [ ] Review a sample of sales orders for accuracy.
- [ ] Match invoices to sales orders and payments.
- [ ] Check for any aging unpaid invoices and escalate follow-up.
B. Standardize Your Processes: Build Your Foundation
- Document Every Step of Your Current Order Process: Before you can improve, understand how it works today. Track who handles each step, how long it takes, where handoffs occur, tools used, and common delays or errors. Create a simple flowchart.
- Create Clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Document the “right” way to handle each step, detailed enough for a new employee.
- Essential SOPs: New order processing, order fulfillment, invoice generation, payment processing, customer communication templates.
- Why Standardization is Crucial: Eliminates “tribal knowledge,” speeds up training, improves quality, decreases errors, and increases scalability.
C. Centralize Your Order Data: Create Your Single Source of Truth
- Moving Away from Spreadsheets and Scattered Notes: Track orders in one centralized system accessible to your entire team.
- Benefits of Centralized Order Data: Real-time visibility, elimination of duplicate data entry, reduced errors, better customer service, and improved reporting.
- What “Centralized” Looks Like: The System should contain customer contacts, product catalog, order history, invoice/payment records, shipping info, and communication history.
D. Automate Repetitive Tasks: Work Smarter, Not Harder
- Identify What CAN Be Automated: Tasks that happen the same way every time (order confirmations, invoice generation, payment reminders, shipping notifications, inventory alerts, status updates).
- Basic Automation: Start Simple: Use email templates, calendar reminders, and features in invoicing software.
- Intermediate Automation: Dedicated Tools: Consider CRM systems, Order Management Software (OMS), and inventory management systems as your business grows.
- Key Principle: Start simple and add complexity only when benefits clearly outweigh costs.
E. Optimize Inventory Management: Balance Cash Flow and Availability
- Just-In-Time (JIT) vs. Safety Stock Strategy: Aim for enough inventory to meet demand without tying up excessive cash. A balanced approach includes core inventory (30-45 days of fast-movers), safety stock (10-15 days for critical products), and seasonal adjustments.
- Regular Inventory Counts and Reconciliation: Physical counts should match system records. Implement cycle counting, ABC analysis (count high-value items more frequently), and investigate variances.
- Using Sales Data to Forecast Demand: Analyze seasonal patterns, growth trends, and product lifecycles.
- Direct Cash Flow Impact: Reduces carrying costs, prevents stockouts, enables bulk discounts, and minimizes obsolescence.
F. Streamline Payment Collection: Accelerate Your Cash Cycle
- Clear and Upfront Payment Terms: Include terms on all quotes/invoices (“Net 30,” “Due upon receipt”) and discuss them during sales conversations. Get agreement in writing.
- Offer Early Payment Discounts (When Feasible): A 2% discount for payment within 10 days can significantly improve cash flow if margins allow.
- Implement Automated Payment Reminders: Set up systematic reminders (e.g., 3 days before due, on due date, and overdue follow-ups at 7, 15, 30 days).
- Make It Easy for Customers to Pay: Offer multiple payment options (credit cards, ACH, checks), online payment portals, mobile-friendly systems, and clear payment instructions.
- Establish a Clear Process for Overdue Accounts: Define an escalation process (automated reminders, personal calls, demand letters, potential collection actions).
G. Improve Communication: Keep Everyone in the Loop
- Customer Communication Standards: Proactive communication prevents most issues.
- Order confirmation within 2 hours (with expected ship date).
- Shipping notification (with tracking and expected delivery).
- Delivery confirmation (follow up for satisfaction).
- Proactive updates for any delays or issues.
- Internal Team Communication: Ensure seamless handoffs between departments (sales to operations, operations to finance, finance to sales). Hold regular team meetings to discuss issues.
H. Leverage Technology Wisely: From Basic Tools to OMS
- When to Consider Software Solutions: Invest when manual processes cause significant delays, frequent errors, limit growth, or consume disproportionate staff time.
- Types of Relevant Software:
- Accounting Software with Invoicing (Starting Point): Tools like QuickBooks or Xero for basic invoicing, payment tracking, and financial reports.
- Inventory Management Software (For Stock-Heavy Businesses): For real-time stock tracking, reorder alerts, PO generation, and multi-location management.
- Order Management Systems (OMS) – The Complete Solution: Purpose-built for end-to-end order processing, real-time tracking, integrations, customer portals, and automated communication.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manage customer lifecycle, lead tracking, interaction history, and sales pipeline.
- E-commerce Platforms (For Online Sales): Shopify or BigCommerce include built-in order management for online channels.
- Tips for Choosing Software: Prioritize ease of use, integration capabilities, scalability, support quality, and total cost of ownership (setup, training, ongoing fees).
I. Track Key Metrics: Measure What Matters
“What gets measured gets managed.” Tracking the right metrics helps identify problems and quantify improvements.
- Essential KPIs for Order Management:
| KPI | Definition | Why It’s Important | Target for Small Businesses |
| Order Processing Time | The total time elapsed from when an order is received to when it is shipped. | Indicates operational efficiency. Faster processing leads to quicker fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction. | 24-48 hours |
| Order Accuracy Rate | The percentage of orders fulfilled and shipped without any errors. | High accuracy reduces costly returns, builds customer trust, and protects profit margins. | 98%+ |
| On-Time Shipping Rate | The percentage of orders shipped by the promised or agreed-upon date. | Crucial for customer satisfaction and loyalty. Late shipments can lead to negative reviews and lost business. | 95%+ |
| Average Invoice Collection Period (DSO) | The average number of days it takes to collect payment after a sale is made. | Directly impacts cash flow. A lower DSO means cash is available sooner for operations and growth. | Match or beat payment terms (e.g., <30 days for Net 30 terms) |
| Inventory Turnover Rate | How many times inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. | Shows how efficiently inventory is managed. Higher turnover means less cash tied up in stock and reduced holding costs. | Varies by industry; aim for higher than industry average |
| Customer Satisfaction Metrics (CSAT, NPS, Repeat Purchase Rate) | Measures of customer happiness with the order process and overall experience. | Indicates how well your processes meet customer expectations. High satisfaction drives loyalty and referrals. | Consistent improvement; positive trends |
- Using KPIs to Drive Improvement: Review metrics monthly. Ask which are trending negatively, what process changes could improve them, where to focus efforts, and how to prevent recurring issues.
Getting Started: Your Action Plan
Don’t try to fix everything at once. Sustainable improvement comes from methodical, step-by-step changes.
- Assess Your Current Process Honestly: Spend one week documenting your actual order management process. Track step durations, error frequency, frustration points, information loss, and common customer complaints. Be brutally honest.
- Identify ONE or TWO Key Areas for Initial Improvement: Based on your assessment, choose areas with the biggest impact (e.g., payment collection if cash flow is tight, order accuracy if losing customers, standardization if volume is an issue).
- Research Tools (If Applicable): If software could help, start researching. Focus on tools addressing specific pain points, consider implementation time, and factor in total costs. Start simple.
- Involve Your Team: Get input and buy-in. Ask for their ideas, address concerns, provide training, and recognize contributions.
- Implement Changes and Monitor Results: Roll out changes systematically, perhaps with pilot programs. Track key metrics and gather feedback from customers and your team. Document learnings.
- Iterate and Continuously Improve: Order management optimization isn’t a one-time project. Review processes quarterly, stay current with technology, benchmark against competitors, and seek customer feedback.
Downloadable Order Management Templates to Get You Started:
To help you implement these practices, here are some essential templates you can adapt:
- Purchase Order Template: A ready-to-use document including fields for supplier details, item descriptions, quantities, agreed prices, payment terms, and delivery instructions to ensure clarity and professionalism in your procurement process.
- Sales Order Template: A ready-to-use document for recording customer orders, including fields for customer information, item details, quantities, pricing, sales terms, and shipping instructions to ensure accurate order processing and clear communication.
- Order Fulfillment Checklist: A step-by-step guide to ensure all tasks in the order fulfillment process are completed accurately and efficiently, covering picking, packing, shipping, and quality checks to minimize errors and enhance customer satisfaction.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Orders, Take Control of Your Business
Implementing a streamlined order management process isn’t just about being more organized; it’s about building a more resilient, profitable, and scalable business. By understanding the core components, avoiding common mistakes, leveraging the right tools, and committing to ongoing optimization, you can transform your order handling from a source of stress into a powerful driver of your company’s success.
Remember, small, consistent improvements compound over time. A business that improves its order management by just 1% each month will see dramatic improvements over a year. The key is to start now and maintain momentum through steady, methodical progress.
Your order management system is the engine that converts customer interest into cash flow. Investing time and resources in optimizing this system pays dividends through improved profitability, customer satisfaction, and business growth potential. The question isn’t whether you can afford to improve your order management—it’s whether you can afford not to.






