A ledger is a financial book containing a written or digital record of all completed business transactions. It is used for posting and balancing cash transactions in a summarized pattern in a business during its financial year.
Together we will go through everything you need to know.
What Is A Ledger Account?
A ledger account often refers to a general ledger – used by various companies to summarize and organize all of their records in the accounting system.
In the past – a ledger was a large book with financial information [bookkeeping] recorded by hand. But in modern times, as the records by hand became complex and time-consuming, the use of bookkeeping software came to light.
Sub-ledgers vs. General ledgers
Sub-ledgers are books used to document business transactions whereas, general ledgers are used as the master notebook to summarize information from the sub-ledger. Here are a few examples of a sub-ledger:
- Inventory: Is a current asset with all the items, goods, and materials held by business owners for selling to their clients to earn profit [asset account].
- Accounts receivable: Refers to the number of money buyers owe to sellers for their purchases [asset account].
- Cash and cash equivalents: Are liquid assets your company owns that are readily cashable [equity account].
- Accounts payable: Accounts payable are any sum of money owed by a business to its suppliers [expense account].
There are five categories of the general ledger;
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Revenue
- Expenses
Let us go through the different categories of a general ledger:
- Assets: These are resources owned or controlled by business owners/ individuals to produce positive economic value.
- Liabilities: Liabilities are future financial debt and obligations of the business. They represent a creditor’s claim on business assets. Examples are taxes, employee wages, mortgages, e.t.c.
- Equity: There exists both positive and negative equity. If the proportion of assets is more than that of the liabilities, it is a case of positive equity. An opposite situation is called negative equity.
- Revenue: This refers to income earned by business owners through the sale of their goods and services. These include all earnings made by business such as sales royalties, e.t.c.
- Expenses: This occurs when a business owner pays in return for goods and services purchased. Examples are rent, travel expenses, e.t.c.
How Do You Write A Ledger?
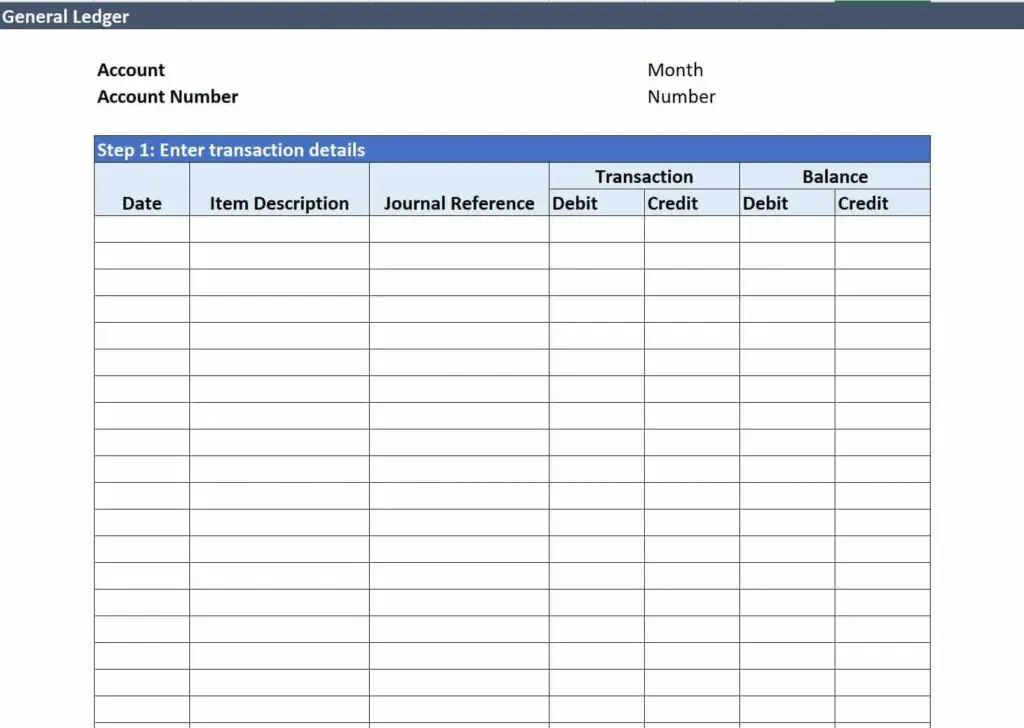
Here are steps on how best to write a ledger:
- For each account you are working on, make a ledger. For unusual or odd expenses – create a general ledger account.
- Create columns on the far left of the page for the date, journal number, and description.
- Create columns on the left side for debit, credit, and balance; Debit refers to the money you receive, credit refers to the money you paid or owed. Balance is the difference between both.
- Input the information from the journals into related accounts; Place debits and credits side by side. Calculate the balance you have earned or owe.
- Document and adjust changes to the transactions as they occur. For example, If you have made a journal entry, post it to the ledger instantly.
- Combine the different accounts to make a complete ledger. The front page includes the chart of accounts, listing each account in the ledger and its number.
- Preparing a trial balance is the next step in an accounting period. The trial balance totals are matched and used to organize financial statements.
What is a Journal?
A journal keeps a record of all transactions made in a business. It is a book of the original entry because if any financial transaction occurs, the business owner/accountant will first record this transaction in its journal.
Journal vs. Ledger
The difference cuts across multiple areas:
- Recording/ documentation: Recording of transactions in the journal happens in the first stage of accounting. On the other hand, in the case of a ledger, it occurs in the second stage.
- Nature: In nature, a ledger is a book of final entries, whereas, in the journal, they are books of original entries.
- Use: Journals are used daily to record transactions as they happen, whereas ledgers are used periodically, like monthly or weekly.
- Preparation: Ledgers are prepared on the basis/ information from journals whereas, journals are based on the source documents.
- Balancing: Journals can’t be balanced, whereas all accounts will be balanced in the ledger, except nominal accounts, e.t.c.
Why are Ledgers important?
They are important because,
- Calculation of profit and loss in every company: Every company needs to create a profit and loss statement on accounting to determine the position of their financial records as it is impossible to make without creating relevant ledger accounts.
- It saves time: With the feature of all entries recorded in one place, it becomes less time-consuming in preparing accounts like trading, profit, and loss.
It’s imperative: Every business owner is obliged to prepare ledger accounts of the parties involved in every transaction for maintaining the correctness or accuracy of the transactions that occurred during the year/ business cycle. You can learn more about the importance of accounting reports in this blog
How Vencru can help your business
Vencru is an invoicing and accounting software that provides accounting reports, invoicing, expense tracking and so much more. Our app is a trusted business solution that is available on the web, android, and iPhones.
Sign up now for our bookkeeping services and make your business more profitable with our 30 days free trial. Don’t have a business yet? See how to create a business plan.